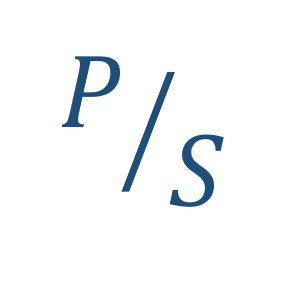A ratio is an option strategy that is created by having X amount of call options at Strike Price 1 and shorting Y amount of call options at Strike Price 2. By creating a ratio, you are creating an option strategy where you can reduce your total option costs by shorting more call options are a higher strike price. Read More…
A straddle is a volatility bet where you simultaneously long a call at Strike Price 1 and long a put at Strike Price 1. This creates a triangular shaped payoff and profit graph where the reward is based on the volatility of the stock. Traders can also bet against volatility by shorting a call at Read More…
A strangle is a volatility bet where you simultaneously long a call at Strike Price 2 and long a put at Strike Price 1. You will notice that the difference with a straddle is the difference strike price for the long call. By buying a call with a higher strike price, you are buying a Read More…
Short Put What is a short put? Recall that a put option is a contract where the buyer has the right (not the obligation) to exercise a sell transaction at a specific strike price before an expiration date. A short put is a term used when you sell a put option for an underlying asset. Read More…
Short Put Recall that a put option is a contract where the buyer has the right (not the obligation) to exercise a sell transaction at a specific strike price before an expiration date. A short put is a term used when you sell a put option for an underlying asset. A trader that has a Read More…
Short Stock What is a short stock? A short stock is an expression used when you sold shares of a company that you did not own beforehand. Let’s say you expect a stock’s price to drop. Shorting a stock would involve a strategy where you borrow shares from another party (usually a broker) and sell Read More…
Long Stock What is a long stock? A long stock is an expression used when you own shares of a company. It represents a claim on the company’s assets and earnings. As you increase your holdings of a stock, your ownership stake in the company increases. Words such as “shares”, “equity” and “stock” all mean Read More…
Understanding financial solvency is as important to an investor as it is to a financial manager. Whether it’s having the money to pay off a friendly wager or having the capital to pay off a commercial loan, being solvent is necessary to achieve long-term success. Solvency is the possession of assets in excess of liabilities, Read More…
Options Spreads are option trading strategies which make use of combinations of buying and selling call and put options of the same or varying strike prices and expiration dates to achieve specific objectives (hedging, arbitrage, etc.). Option spreads are complex trades, but you can place two “legs” simultaneously using this trading platform. Trading Option Spreads To Read More…
Definition “Price Controls” are artificial limits that are put on prices. If the limit is put in place to prevent prices from getting too high, they are called Ceilings. If they are in place to prevent the price from getting too low, they are called “Floors”. Price Ceilings Price Ceilings are controls put in place Read More…
Definition Scarcity refers to the fact that resources are finite – people and organizations need to allocate their finite resources between their infinite wants. Each year, the world produces more goods and services, along with better technologies and processes that can increase output farther. Even with this growth, there will always be scarcity, because there Read More…
Definition “Specialization” is when a labor force begins to divide total production, leading to a rise of experts or specialists. This is called the Division of Labor, and it typically results in much higher productivity of labor. How Does It Work? Specialization has two main parts – Division of Labor, and a rise of Experts. Read More…
Definition “Opportunity Cost” is what needs to be given up to get something. This is different from an item’s price. Imagine you want to buy some stock for your virtual portfolio – you can afford one share of either Apple () or Alphabet, Inc. (). Your Opportunity Cost of buying one is that you cannot also Read More…
Definition of Spending Plan A “Spending Plan” is exactly as it says – a plan of what you will be spending each month. There are usually two parts – your “fixed” spending and your “variable” spending. The fixed part is usually the same every month, with things like rent/mortgage payments, grocery bills, insurance, and car Read More…
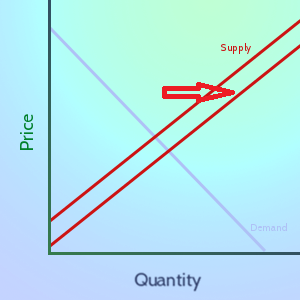
The stock market determines prices by constantly-shifting movements in the supply and demand for stocks. The price and quantity where supply are equal is called “Market Equilibrium”, and one major role of stock exchanges is to help facilitate this balance. We can use the stock market to give some great supply and demand examples with Read More…
Definition In Economics, “Supply” means the relationship between prices and production. In general, the higher the market price of a good or service is, the more producers are willing to sell of it. Details As the market price for a good goes up, companies want to sell more of it to try to make greater profits. Read More…
Definition The Reserve Requirement is how much of all deposits that a bank is required to keep “on hand”, meaning in its vaults, or on deposit at the Federal Reserve Bank (in the United States). Details The “Reserve Requirement” is about 10% of all money that has been deposited at a bank. Because of how Read More…
Definition The stock market crash of 1929 was a massive crash in stock prices on the New York Stock Exchange, and marks the largest financial crash in the United States. Details The stock market crash came in multiple parts – the initial crash on October 28 (a 12.87% drop) continued into October 29 (a 11.73% drop), Read More…
Definition “OHLC” stands for “Open, High, Low, Close”, and this is a chart designed to help illustrate the movement of a stock’s price over time (typically a trading day, hour, or minute) Details OHLC charts are also known as “Bar Charts” because they display the information as a series of line segments instead of as Read More…
Definition Spot and Futures contracts are a standardized, transferable legal agreement to make or take delivery of a specified amount of a certain commodity, currency, or an asset at the current date. The price is determined when the agreement is made. The only difference between spots and futures is the delivery date. The current date Read More…
Definition A stock quote gives essential information about a particular stock at a point in time. The quote normally includes information such as the name of the company, the ticker symbol, the price, the day’s high and low prices, and the trading volume. Details Usually when you get a stock quote, you see lots of Read More…
Definition: A “Ticker Symbol” is a unique one to five letter code used by the stock exchanges to identify a company. It is called a ticker symbol because the stock quotes used to be printed on a ticker tape machine that looked like the images below. When it printed the stock quotes, it made a tick-tick-tick Read More…
Definition: The New York Stock Exchange (or NYSE) is the largest stock exchange in the world. Think of it as an organized, fast-paced flea market where buyers and sellers from all over the world come to trade U.S. stocks (and now some foreign shares as well). It is where over 2,800 of the biggest U.S. Read More…
What is a Stock? Stock is defined as a share of ownership in a company. If you own a company’s stock, you own a percentage of the company itself. This includes partial ownership of its assets (like equipment, vehicles, and buildings) and partial ownership if its income and profits. The main reason people purchase stock Read More…
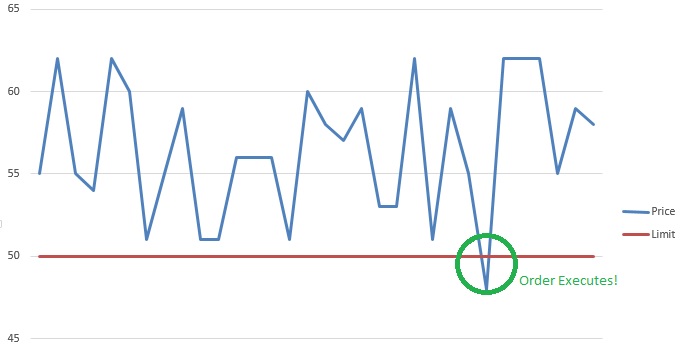
Definition A Stop (or stop loss) order and limit order are orders that try to execute (meaning become a market order) when a certain price threshold is reached. Limit and stop orders are mirrors of each other; they have the same mechanics, but have opposite triggers. When creating a limit or stop order, you will select Read More…
Definition An order type that allows to set a moving stop or limit target price. The target price moves based on the daily high. Trailing stops can be set either in percentage or in dollars and cents terms. When in dollar terms it will activate when the price has moved by the target you have Read More…
Definition Your “Risk Level” is how much risk you are willing to accept to get a certain level of reward; riskier stocks are both the ones that can lose the most or gain the most over time. Risk Understanding the level of risk you need and want is a very important part of selecting a Read More…
Definition Open Interest is the total number of options or futures contracts that are “open”, meaning currently owned by an investor and not yet expired. Details Think first in terms of options contracts: by owning an option, it signifies that there is interest in actually trading that stock, although at a different price. Since this Read More…
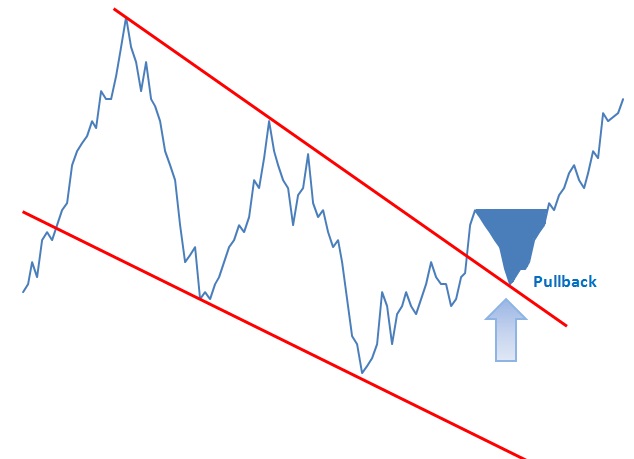
A pullback is a technical analysis term used frequently when a stock “pulls” back to a resistance and/or support line, usually after a breakout has occurred. Pullbacks can be in an uptrend or downtrend and can pull back upwards or downwards. In the example below we can see a pullback as it retraces back to Read More…
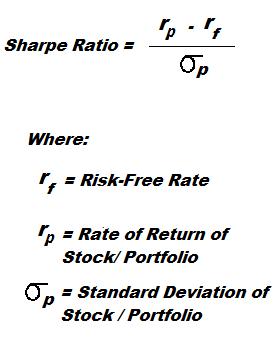
Sharpe Ratio for Beginners Introduction The Sharpe Ratio is an important tool for evaluating a stock, or a portfolio, based on how risky it is to get a higher return. You can use the Sharpe Ratio to determine how consistent the returns of a stock or portfolio are, so you can determine if the returns Read More…
Over-The-Counter (OTC) Stocks Most investors are familiar with NASDAQ, the NYSE (New York Stock Exchange), TSX (Toronto Stock Exchange), and most other large national stock exchanges. However, there are also thousands of companies that want to sell shares to the general public, but are not able to sell on these exchanges. Stock traded on these Read More…
Price ceiling is a government-mandated limit on the price that can be charged for a given product, such as a utility or electricity. The intended purpose of a price ceiling is to protect the consumers from conditions that would make a vital product from being financially unattainable for consumers.
A “Poison Pill” creates a strong defense mechanism for a “targeted takeover company” allowing the company to properly identify legitimate and beneficial acquisitions and weed out the actions of corporate raiders. The “Poison Pill” is also useful in slowing down the speed of potential raids.
An oligopoly is characterized by a small number of sellers who dominate an entire market.
Straight line depreciation is the most commonly used and simplest form of depreciation.
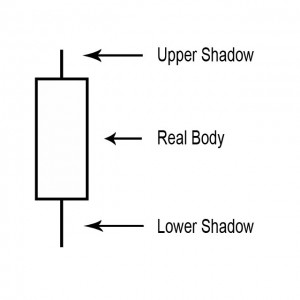
A small line (like a candle wick) found at the top or bottom of an individual candle in a candlestick chart.
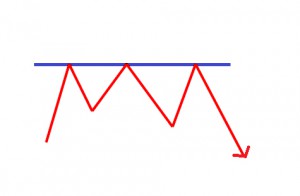
A point or range in a chart that caps an increase in the price of a stock or index over a period of time. An area of resistance, resistance line or resistance level indicates that the stock or index is finding it difficult to break through it, and may head lower shortly. The more times that the stock or index tries unsuccessfully to break through the resistance line, the stronger that area of price resistance becomes.
The price-to-sales ratio (Price/Sales or P/S) provides a simple approach: take the company’s market capitalization (the number of shares multiplied by the share price) and divide it by the company’s total sales over the past 12 months. The lower the ratio, the more attractive the investment.
High inflation and high unemployment occurring simultaneously.
Return on Equity (ROE) is used to measure how much profit a company is able to generate from the money invested by shareholders.
Price to Earnings is the most usual way to compare the relative value of stocks based on earnings since you calculate it by taking the current price of the stock and divide it by the Earnings Per Share (EPS).
Stock volatility information can be used in many different ways but here is a quick and easy bit of stock volatility information that you can begin using today.
Small cap stock investing is volatile. That is one of first things you should know and understand. So, why risk your money by investing in what is typically considered risky business?
Market risk is a measure of how much of a loss an investor is facing while trading.
Everywhere you turn there is another proprietary stock market timing system being sold. Let’s take a few minutes to review these claims against common sense.
It is only an offer and will not be accepted if the seller is not willing to let go at the offer price. This offer price pertains to all traded investments.
The difference between the ask price and the sell price is called the “spread” and it is kept by the broker.
If you are brand new to investing then take time to understand what you are reading when viewing a Stock Exchange Symbol and learn Stock Market Investing Basics.
Many people start trading stocks and never learn about stock trading risk management. The one’s that do learn, usually learn after they have been trading for a while, not before they start trading.
A REIT or Real Estate Investment Trust may be the perfect investment vehicle. REITs own, and often operate, real estate but are publicly traded like stock.
By measuring the compilation of similar stocks instead of just one or two stocks, a stock index provides information about that particular market or segment.
Many stock analysts have identified market trends related to specific times of the year. The success ratios of these trends are often far stronger than most other indicators.
Simplest, oldest, and most common form of business ownership in which only one individual acquires all the benefits and risks of running an enterprise. In a sole-proprietorship there is no legal distinction between the assets and liabilities of a business and those of its owner. It is by far the most popular business structure for startups because of its ease of formation, least record keeping, minimal regulatory controls, and avoidance of double taxation.
Retained earnings is calculated by adding net income to (or subtracting any net losses from) the beginning retained earnings and then subtracting the dividends that were paid to shareholders
The total amount that the federal government has borrowed including internal debt (borrowed from national creditors) and external debt (borrowed from foreign creditors).
A Stop Limit is an order that combines the features of stop order with the features of a limit order. A stop limit order executes at a specified price (or better) after a specified stop price is reached. After the stop price is reached, the stop limit order becomes a limit order to buy (or sell) at the limit price or better.
US federal legislation of 1890 that prohibited the creation of monopolies by outlawing direct or indirect attempts to interfere with the free and competitive nature of the production and distribution of goods. Amended by the Clayton Act of 1914. Also called Sherman Act.
Resistance and support levels are widely used by experienced traders to formulate trading strategies. For example, if a stock is approaching a very strong resistance level, a trader may prefer to close the position rather than take the risk of a significant decline if the stock uptrend reverses.
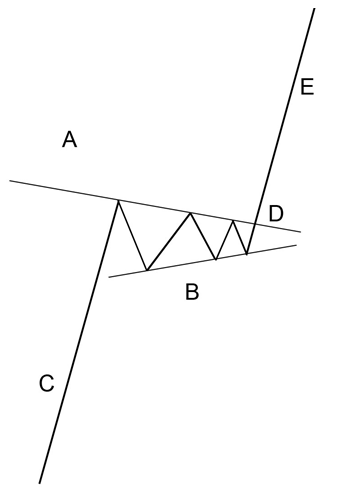
The pennant resembles the symmetrical triangle, but it’s characteristics are not the same. The pennants is shaped like a wedge of consolidation. Its normally appears after a sudden upward or downward movement. The life of a pennant is short according to the time frame used.
A trailing stop loss is calculated in a manner like the way we calculated our initial stop loss. The only difference being that while we calculated our stop loss from the entry price, we’re calculating our trailing stop loss from the highest price since entry.
Order Types offered in our Stock Market Game: Market Orders, Limit Orders, Stop Market Orders, Stop Limit Orders and Trailing Stop Orders
Penny stocks are stocks with a share price of $5 or less.
A tool that investors and traders can use to filter ETFs based on user-defined metrics. ETF screeners are offered on many websites and trading platforms, and they allow users to select trading instruments that fit a certain profile set of criteria.
A Trading Halt is the temporary suspension of trading of a security for a specific period of time. Trading Halts typically last for an hour, but can extend into days.
Time Decay is the inclination for options to decrease in worth as the expiration date draws near. The extent of the time decay is inversely connected to the changeability of that option.
A Sharpe Ratio calculates the extra return you make compared to the extra risk you take on.
The basic form of short selling is selling stock that you borrow from an owner and do not own yourself. In essence, you deliver the borrowed shares. Another form is to sell stock that you do not own and are not borrowing from someone. Here you owe the shorted shares to the buyer but “fail to deliver.”
The cash received from the short sale of a security. The interest return from investment of the short proceeds is usually divided between the short seller, who gets partial “use of proceeds,” and the securities lender.
In finance, short selling (also known as shorting or going short) is the practice of selling securities or other financial instruments, with the intention of subsequently repurchasing them (“covering”) at a lower price. In the event of an interim price decline, the short seller will profit, since the cost of repurchase will be less than the proceeds received upon the initial (short) sale. Conversely, the short seller will incur a loss in the event that the price of a shorted instrument should rise prior to repurchase.
An order placed with a broker to sell a security when it reaches a certain price. A stop-loss order is designed to limit an investor’s loss on a security position.
A stop order is an order to buy or sell a stock when the stock price reaches a specified price, which is known as a stop price. When the specified price is reached, the stop order becomes a market order.
Preferred stock is a special class of stock issued by a company that pays dividends. Preferred stock is more like a bond than true stock because the main appeal is dividend income. Most preferred stocks are limited in the total profit they can earn.
Technical Analysis is the use of technical indicators comprising of statistics using past market information to predict which direction the security price will move.
Trailing Stop is a Stop Loss order which is placed as a percentage value as opposed to an absolute dollar value. The order will only execute if the price of the security falls by a certain percentage. The trailing stop adjusts automatically as the price of the security rises and bases itself on the new appreciated value. This type of order allows profits to be made while cutting losses simultaneously.
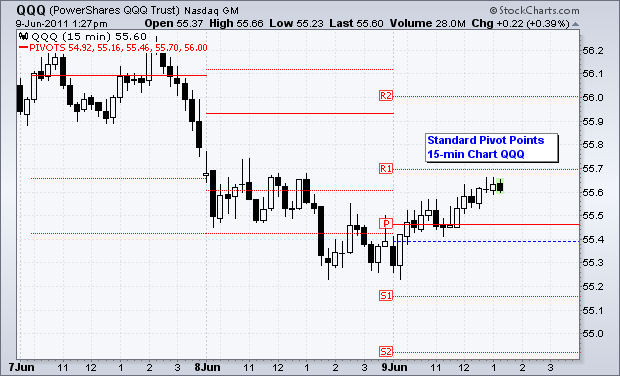
Pivot Points use the previous period’s high, low and close which will define future support and resistance. Pivots Points are important levels chartists utilize to decide directional movement, resistance and support
A Trailing Stop is an order to close out your position if the price goes against you by a certain percentage or dollar value. It is different to a normal stop order as the stop price moves in your favour if the price of the stock moves in the direction you want it to. This Read More…
A dollar Trailing Stop is a Stop Loss order which is placed as a dollar value. The order will only execute if the price of the security falls by that dollar amount. The trailing stop adjusts automatically as the price of the security rises and bases itself on the new appreciated value. This type of Read More…
Treasury bills, often referred to as T-bills, are short-term securities (maturities of less than one year) offered and guaranteed by the federal government. They are issued at a discount and pay their full face value at maturity.
A percentage Trailing Stop is a Stop Loss order which is placed as a percentage value as opposed to an absolute dollar value. The order will only execute if the price of the security falls by a certain percentage. The trailing stop adjusts automatically as the price of the security rises and bases itself on Read More…
Tick refers to a change in price, either up or down.
S&P 500 Index (Standard and Poor’s 500 Index) is a composite of the 500 most actively traded public companies in all ten economic sectors of the U.S. It is maintained by Standard and Poor’s, a division of the Parent company McGraw-Hill.
Selling Short is a trade in which the investor borrows a security and sells it to another investor in the market. To close the short position an investor has to cover (purchase the same security from the market) and return it to the person they borrowed it from.
Security is any financial instrument that represents a financial value
Recession is generally described as a slowdown of economic growth over a sustained period of time.
Quick Ratio is the ratio that measures the ability of a firm to cover its current liabilities with their most liquid current assets. Quick Ratio = (Current Assets – Inventory) / Current Liabilities
A Put Option gives the holder the right to sell the underlying stock or futures contract at a specified strike price.
Pink Sheets refer to the trading of stocks that are not listed on a major exchange or the OTCBB due to a lack of minimum listing requirements or filing financial statements with the SEC (Securities Exchange Commission)
Par Value is the amount that the issuer of a bond agrees to pay at the date of maturity.
Out-Of-The-Money refers to an option that is unfavourable to exercise. An example is a put option with a strike price lower than the underlying stock price, or a call option with a strike price higher than the underlying stock price.
An Options Contract is a contract which specifies how much of the underlying asset can be bought or sold at a specific price. An option contract to buy the underlying is a call option, and to sell the underlying is a put option. Most stock options contracts represent 100 underlying shares.
What are they doing with your money? Have you ever wondered how well your money is really being managed by the corporations you hand it over to? After all, the media is full of stories about CEO compensation reaching new heights, buy-outs of non-profitable holdings, million dollar birthday parties and other horror stories. Formula for Read More…
A Sharpe Ratio calculates the extra return of an investment in return for the extra risk taken on. It is used to compare different investments to see which one did better given the different risk of each. It is measured as taking the difference between a risk-free and a risky asset, and then dividing the difference by the Standard Deviation (which Read More…