Comparative Advantage is the concept where one person, business, or economy is able to outproduce one particular product or service compared to another person, business, or economy. The concept of comparative advantage is essential to understanding both why people choose different careers, and why countries engage in international trade. Comparative Advantage At The Personal Level Read More…
In Economics, “Gross Domestic Product” is the one statistic to rule them all – a measure of the total size of an economy. Definition The “Gross Domestic Product” of a country is the total value of all finished goods and services that were produced in a given year. In other words, this is the total Read More…
Property rights is the foundation of all free-enterprise economic systems. It is what allows people to profit from capital and ideas, without fear of seizure by the government or theft. Definition “Property Rights” usually refers to a set of fundamental rights giving citizens control over their own land, capital, and ideas. Land Property Rights The Read More…
International Trade is the system under which businesses, individuals, and governments trade goods and services. This exchange from many different National economies is what makes up the Global economy. Imports and Exports When we talk about international trade, we usually think in terms of imports (the goods and services a country buys from outside) and Read More…
Inflation: how much less a dollar is worth next year compared to today. Most consumers hate inflation – it erodes your savings, and eats away at the real benefits you get from increasing income. However, inflation plays a necessary role in the economy, and without it much of the economy would quickly fall apart. Inflation Read More…
As a society with a market-based economy, the government has three broad mandates: Ensure the common defense Promote economic growth Strive to maintain a just society On the face, only one of these implies direct intervention in the economy, but all three are interconnected with the economy as a whole. This means every action taken Read More…
Government spending makes up a whopping 20% of all spending in the American economy, including the salaries of all government employees, government contracts to private companies, and military spending. This is all paid for by taxes, meaning more than 1/3 of all economic activity filters through the public sector in some way. This means government Read More…
The “Time Value of Money” is one of the most important concepts in economics, investing, and business. For individuals, this determines how much you save and spend. For businesses, it determines how quickly they try to expand. For investors, it decides the mix of a portfolio. What is the Time Value of Money? “Time is Read More…
What is “Labor”? “Labor” is how much a person works. It is the use of time and exertion of effort to produce something of value. Generally speaking, the more valuable a person’s labor is, the higher their wage. Skilled And Unskilled Labor Each person starts off as an Unskilled Worker, meaning they do not have Read More…
“Unemployment” is a major economic indicator measuring how much of the working population is currently looking for a job. The unemployment rate is the most “tangible” economic indicator – if GDP is going up or down, it is harder for people to notice in their day-to-day lives. When the unemployment rate goes up, it usually Read More…
Definition “Price Controls” are artificial limits that are put on prices. If the limit is put in place to prevent prices from getting too high, they are called Ceilings. If they are in place to prevent the price from getting too low, they are called “Floors”. Price Ceilings Price Ceilings are controls put in place Read More…
What Are Interest Rates? Interest rates are growth rates – it is a percentage that is used to calculate how much a loan or investment grows over time. Interest rates are most commonly associated with borrowing money, like a homeowner taking out a mortgage or a government selling a bond. The interest rate is how Read More…
Definition Scarcity refers to the fact that resources are finite – people and organizations need to allocate their finite resources between their infinite wants. Each year, the world produces more goods and services, along with better technologies and processes that can increase output farther. Even with this growth, there will always be scarcity, because there Read More…
Definition “Specialization” is when a labor force begins to divide total production, leading to a rise of experts or specialists. This is called the Division of Labor, and it typically results in much higher productivity of labor. How Does It Work? Specialization has two main parts – Division of Labor, and a rise of Experts. Read More…
Definition “Opportunity Cost” is what needs to be given up to get something. This is different from an item’s price. Imagine you want to buy some stock for your virtual portfolio – you can afford one share of either Apple () or Alphabet, Inc. (). Your Opportunity Cost of buying one is that you cannot also Read More…
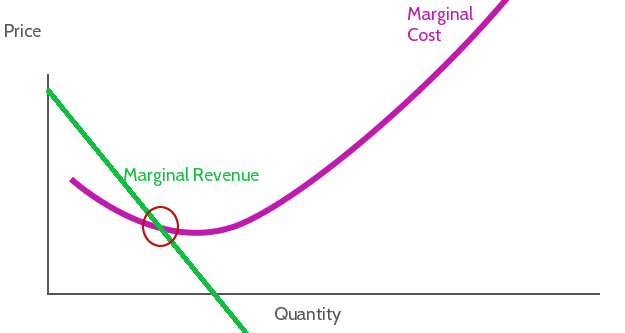
Everyone knows about costs and benefits of doing something – the pros and cons of making a choice. Marginal benefit and marginal cost are different – they look more closely at doing slightly more or less of different alternatives. Marginal costs and benefits are extremely important to producers when choosing their inputs and prices. [gtranslate] Read More…
What is Competition? “Competition” is when many producers try to sell similar goods to the same set of consumers. The producers need to “compete” to try to attract more consumers, usually by lowering prices, offering better versions of the goods or services, or through marketing. Competition is the core concept of the Market Economy. Why Read More…
What Is The Business Cycle? The Business Cycle is the broad, over-stretching cycle of expansion and recession in an economy. The Business Cycle is concerned with many things – unemployment, industrial expansion, inflation rates, but the most important indicator is GDP (Gross Domestic Product) growth. Below you can see a graph of the GDP growth Read More…
What does it mean to be an Entrepreneur? An Entrepreneur is someone who takes a risk to start a new business. Nearly every business that exists (apart those created as spin-offs of other businesses, or by government intervention) was started by one or several entrepreneurs, who took a risk to launch a new company. Who becomes Read More…
Definition Economic Incentives includes anything that pushes people, businesses, and governments to do one thing or another. This includes what products you buy, what career you choose, what products businesses produce, and what government programs are put in place. Incentives for Individuals Each individual faces many economic incentives every day. If you are in school, Read More…
Definition In Economics, an “Externality” is a benefit or cost that is not reflected in the price of a good or service. Why do Externalities Exist? Prices are determined by the relationship between the supply and demand of a good or service (for details, see our article on Supply and Demand Examples in the Stock Read More…
What is Economic Growth? Economic Growth means that the economy is growing – more goods and services are being produced and consumed than they were before. The most common measurement of economic growth is the Gross Domestic Product (or GDP), which measures the total number of finished goods and services produced in an economy in Read More…
Definition “Economics” is often called the Dismal Science – it studies the trade-offs between making choices. The purpose of economics is to look at the different incentives, assets, and choices facing people, businesses, schools, and governments, and see if there is any way to improve outcomes. This is done by looking at how supply and Read More…
Have you ever wanted to start a business? Maybe you want to know the difference between a lemonade stand and Minute-Maid, besides just the size of the companies. Different types of companies have different levels of liability (meaning level of responsibility) for the owner or owners. What this means is that the more liability an owner has, Read More…
Definition “Major Economic Indicators” are numbers that you can look at to try to get a picture of how well the economy is doing. Different indicators measure different parts of the economy, but their main characteristic is that they measure the same thing in the same way over time. This means that you can compare the Read More…
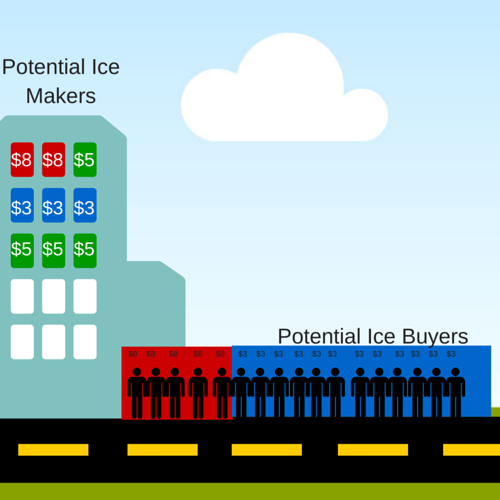
The stock market determines prices by constantly-shifting movements in the supply and demand for stocks. The price and quantity where supply are equal is called “Market Equilibrium”, and one major role of stock exchanges is to help facilitate this balance. We can use the stock market to give some great supply and demand examples with Read More…
Comparing Economic Systems There are many different economic systems that try to result in more equality or faster growth. The structure of a country’s economy has a lot to do with the country’s politics and the values of its population. However, the economy of every country also changes over time, and how it falls between Read More…
Definition The Federal Reserve Bank, or the “Fed”, is the central banking system of the United States. It serves as the primary regulator of the US dollar, as well as the “lender of last resort” for other banks. Regulating Currency The Federal Reserve works to maintain the interest rates that banks use to lend money to Read More…
Gross National Product is the value of all goods and services produced by a country’s residents.
Price ceiling is a government-mandated limit on the price that can be charged for a given product, such as a utility or electricity. The intended purpose of a price ceiling is to protect the consumers from conditions that would make a vital product from being financially unattainable for consumers.
An oligopoly is characterized by a small number of sellers who dominate an entire market.
Monopoly, in economic terms, is used to refer to a specific company or individual has a large enough control of a particular product or service that allows them to influence it’s price or certain characteristics.
Monopolistic Competition is characterized as a form of imperfect competition.
Money supply is the total amount of money available in an economy at any particular point in time.
Monetary Policy refers to the process by which the Monetary Authority of a given country implements a variety of measures to control the supply of money.
Fiscal policy is the use of government spending to influence the economy.
Elasticity is one of the most important terms in economics, and has a plethora of uses. Economists define elasticity as the ratio of the percent change in one variable to the percent change in another valuable.
A consumer price index (CPI) is the relative measure of a market basket of consumer goods and services purchased by households.
High inflation and high unemployment occurring simultaneously.
Hyperinflation refers to out of control or extremely rapid inflation, where prices increase so quickly that the concept of real inflation becomes meaningless.
The Fed is the US central-banking system which is made up of 12 regional central banks
The total amount that the federal government has borrowed including internal debt (borrowed from national creditors) and external debt (borrowed from foreign creditors).
Stock prices are a direct result of supply and demand. All the other influences like debt, balance sheets, earnings and so on affect the desirability of owning (or selling) a stock.
Decreasing the long-run average and marginal costs that come from an increase in the size of a factory or plant.
Recession is generally described as a slowdown of economic growth over a sustained period of time.